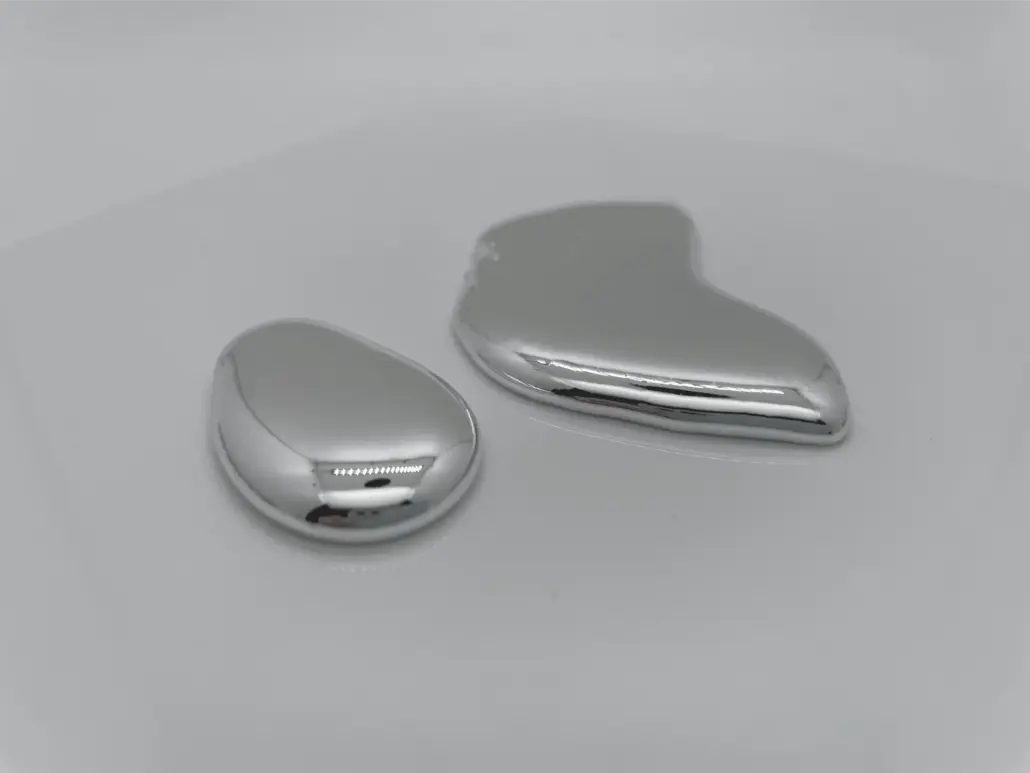
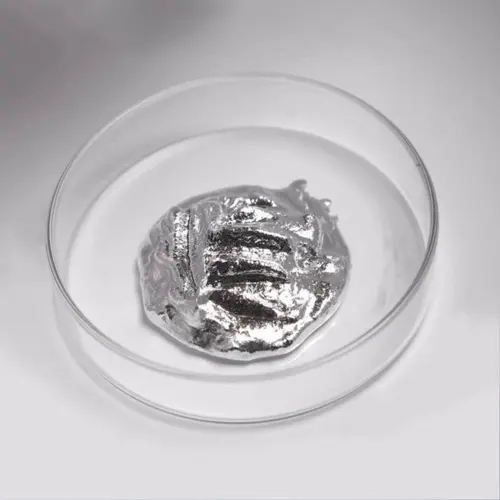
Liquid metal, also known as liquid metal thermal conductor or liquid metal coolant, is a type of cooling medium composed of low-melting-point alloys. It has a high specific heat capacity, high thermal conductivity, low melting point, and high boiling point. Currently, it is primarily used in fields such as nuclear reactor heat conduction and computer…
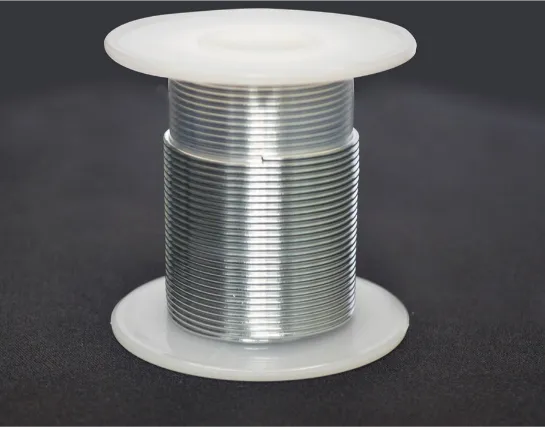
Indium Wire, made from high-purity indium metal, is prized for its exceptional malleability and thermal conductivity. Its low melting point and high ductility make it a preferred choice for soldering applications, particularly in electronics and semiconductor industries, ensuring dependable connections. With its compatibility across various materials and low reactivity, Indium Wire is ideal for bonding…
When it comes to optimizing thermal conductivity in high-temperature and cryogenic applications, two standout solutions emerge: Indium Foil and Liquid Metal Thermal Paste. Let’s delve into their unique properties and applications to understand their comparative advantages. Indium Foil, crafted from pure Indium Ingot, boasts exceptional malleability and a remarkable thermal conductivity of 86W/mK. Its versatility…
Recycling waste indium wire not only helps reduce the demand for limited indium resources but also aids in minimizing waste generation, thus alleviating environmental impacts. Below are some common methods for recycling waste indium wire: Physical Separation and Purification: Physical separation is one of the most common methods for recycling waste indium wire. In…
In today’s advancing electronic devices, efficient heat dissipation is a critical consideration in design. Introducing our Indium Tin Alloy Sheet, designed to meet the demanding heat dissipation needs of high-power devices, offering a reliable solution for your high-performance equipment. Crafted from premium indium tin alloy material, our Indium Tin Sheet boasts exceptional thermal conductivity…
In the realm of high-power devices like LEDs, lasers, and expansive server rooms, efficient heat dissipation is paramount for optimal performance and longevity. Understanding the pivotal role of thermal conductivity and the materials involved is key to maximizing cooling efficiency. The Importance of Thermal Conductivity: At room temperature, materials with higher thermal conductivity facilitate faster…
Indium wire is a type of fine wire made of pure indium, typically characterized by high purity and good conductivity. The Mohs hardness of metallic indium is only 1.2, much lower than the Mohs hardness of copper (2.5-3) and aluminum (2-2.9), with a melting point of 156.6°C. Its excellent ductility makes it very advantageous for…
Indium foil, a remarkable thermal interface material (TIM), offering superior heat dissipation for components like CPUs. Its efficient heat transfer enables smaller cooling systems, prolonging battery life. Moreover, its soft, ductile nature ensures better surface coverage, reducing airflow gaps and enhancing heat flow. Unlike paste or grease, this indium foil remains intact over time, maintaining…
Indium alloys offer a spectrum of possibilities, ranging from binary to ternary and multicomponent compositions. As the primary constituent, indium lends these alloys relatively low melting points, making them ideal for applications such as low-melting-point alloys or solders. Beyond mere utility, indium’s presence in some alloys serves to enhance properties like strength, ductility, wear resistance,…
Indium is a metallic element with the chemical symbol In, belonging to the group IIIA of the periodic table. It has an atomic number of 49 and a relative atomic mass of 114.8. Its melting point is 156.61°C, and its boiling point is 2060°C. It has a relative density of 7.31 g/cm³. Indium was discovered…