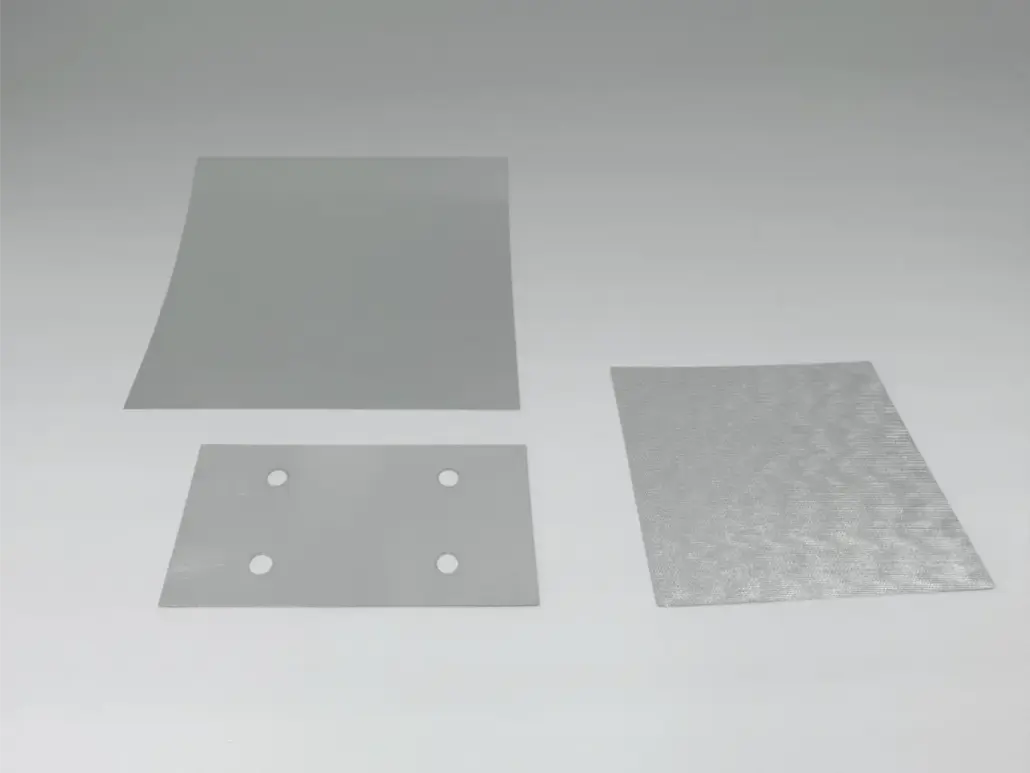
インジウムは、展性と低融点が特徴のポスト遷移金属で、鉛などの従来のはんだに比べて濡れ性が高く毒性が低いことから、さまざまな産業、特にエレクトロニクスで広く利用されています。アルミニウムは、軽量、耐腐食性、優れた導電性で知られており、航空宇宙、自動車、家庭用電化製品で広く使用されているため、接着の研究は接合部品の信頼性を確保する上で非常に重要です。インジウムとアルミニウムの接着は、表面処理、酸化層の存在、環境条件など、さまざまな要因の影響を受けます。濡れ性を高め、機械的連結を促進するさまざまな表面処理技術によって、効果的な接着を実現できます。ただし、…
インジウム箔は、優れた導電性、展性、低融点など、独自の物理的および化学的特性で知られるポスト遷移金属であるインジウムから得られる特殊材料です。1863 年に発見されたインジウムは、さまざまな産業用途、特にエレクトロニクス、再生可能エネルギー、医療技術でますます重要になっています。インジウム箔は、インジウムベースのはんだ、透明導電性コーティング、タッチスクリーンから太陽電池までさまざまなデバイスの高性能コンポーネントの製造に重要な役割を果たしています。現代のテクノロジーにおけるインジウム箔の重要性は、いくら強調してもし過ぎることはありません。その低融点により、熱に弱い電子部品を安全に組み立てることができ、その熱伝導性により冷却システムの性能が向上します…
インジウムを使ったはんだ付けは、融点が低く、延性があり、濡れ性に優れていることで知られるポスト遷移金属であるインジウムのユニークな特性により、注目を集めています。これらの特性により、熱に弱い部品の完全性を維持することが重要な電子機器や医療機器など、さまざまな業界ではんだ付けにインジウムがますます好まれるようになっています。インジウムはんだの汎用性により、繊細な電子回路の組み立てから柔軟な手術器具の作成まで、さまざまな用途に利用でき、重要な用途での安全性と性能の両方が向上します。はんだ付けにインジウムを使用する際立った利点には、冷間溶接が可能であること、鉛フリーのオプションとして環境に優しいこと、優れた熱サイクル耐性などがあります。
インジウムはんだは、さまざまな産業用途、特にエレクトロニクス分野で数多くの利点を提供する特殊な合金です。特に、現代の環境基準に適合した鉛フリーの代替品であり、持続可能な製造方法に対する高まる需要に応えています。低融点、優れた濡れ性、並外れた延性などの独自の特性により、小型電子機器など、信頼性と耐久性のある接続を必要とする用途で好まれています。インジウムはんだの主な利点の 1 つは、融点が低いことです。これにより、はんだ付けプロセス中に敏感なコンポーネントへの熱による損傷が最小限に抑えられます。電子機器が小型化して熱に敏感になるにつれて、この特性はますます重要になっています。さらに、インジウムはんだの…
錫は銀白色の金属で、最初は柔らかいですが、空気にさらされるとすぐに鈍い灰色に変色します。錫は非常に可鍛性があり、壊れることなく簡単に形を作ることができます。また、非常に延性があるため、細いワイヤーに引き伸ばすことができます。錫は、天然の形で見つかる数少ない金属の 1 つであり、鉱石から抽出する必要はありません。これは、錫の反応性が比較的低く、他の元素と容易に化合物を形成しないためです。錫は青銅器時代に早くも人間によって使用され、それ以来、人類の歴史において重要な金属となっています。錫はさまざまな方法で使用できますが、最も一般的なのは錫板の形で見つかります。錫板は薄く、軽量で、耐腐食性があります。錫板の使用を計画している場合は、次のガイドで必要な情報をすべて入手できます。錫板は何に使用されますか?錫板は、食品業界でよく使用されます。…
インジウムはんだ箔は、融点が低く、優れた導電性を持つ多用途の材料で、幅広い業界で使用されています。そのユニークな特性により、特に高性能デバイスの組み立てなど、電子機器での使用に適しています。インジウムはんだ箔の主な利点の 1 つは、比較的低温で強力で信頼性の高い接合を形成できることです。この特性は、繊細な電子部品の組み立てなど、熱に対する敏感性が懸念される用途では非常に重要です。さらに、インジウムはんだ箔は濡れ性に優れているため、均一で一貫したはんだ接合が保証されます。電子機器の分野では、インジウムはんだ箔はプリント回路基板 (PCB) の製造に重要な役割を果たしています。インジウムはんだ箔は、電子部品を PCB トレースに接続し、電流を流すための電気経路を作成するために使用されます。インジウムはんだ箔の融点が低いため、リフローはんだ付けが可能です。リフローはんだ付けでは、PCB を特定の温度に加熱してはんだを溶かして流し、安全な接続を形成します。この方法は、効率性と精度の高さから、電子機器の大量生産で広く採用されています。インジウムはんだ箔は、PCB 以外にも、半導体デバイスの組み立てに使用されています。現代の電子機器の構成要素である半導体は、多くの場合、精密で繊細なはんだ付け技術を必要とします。インジウムはんだ箔は、融点が低く、導電性に優れているため、これらの繊細なコンポーネントを接続するのに最適です。さらに、薄く均一なはんだ接合部を形成できるため、半導体デバイスが損傷するリスクが最小限に抑えられます。自動車業界も、インジウムはんだ箔のユニークな特性の恩恵を受けています。センサー、制御ユニット、インフォテインメント システムなどの自動車用電子機器の製造に使用されています。極端な温度や振動にさらされるなど、車内の過酷な動作条件では、信頼性が高く耐久性のあるはんだ材料を使用する必要があります。インジウムはんだ箔は、これらの条件に耐えられるため、自動車用途に適しています。さらに、インジウムはんだ箔は、医療機器の分野でもますます使用されています。生体適合性と低毒性のため、インプラント デバイスやその他の医療用途に適しています。低温で強力で信頼性の高い接続を形成できる能力は、繊細な医療機器やセンサーの組み立てにおいて特に貴重です。結論として、インジウムはんだ箔は、その低融点、優れた導電性、濡れ性などの特性のユニークな組み合わせにより、さまざまな業界で幅広く採用されています。電子機器や半導体から自動車や医療機器まで、インジウムはんだ箔は、高性能で信頼性が高く革新的な製品を生み出す上で重要な役割を果たしています。技術が進歩するにつれ、より小型で効率的で信頼性の高い電子機器のニーズに後押しされ、インジウムはんだ箔の需要は増加すると予想されます。
インジウム(In)は比較的低い融点(157°C)を持ち、Sn(スズ)、Pb(鉛)、Ag(銀)などの元素と一連の低融点共晶はんだを形成できます。これにより、パッケージングやはんだ付けプロセス中に製品が高温の影響を受けるのを回避できます。インジウムベースのはんだは、アルカリ媒体に対する耐腐食性が高く、金属と非金属の両方に対して優れた濡れ性を備えています。インジウムで形成されたはんだ接合部は、電気抵抗が低く、可塑性が高いなどの利点があり、熱膨張係数の異なる材料のパッケージングに適しています。そのため、インジウムベースのはんだは、主に電子真空デバイス、ガラス、セラミック、低温超伝導のパッケージングに使用されています。
インジウム箔は、主に航空宇宙産業やエレクトロニクス産業で低温で非常に効果的な気密シールを作成するために使用される特殊な材料です。独自の物理的および化学的特性で知られるインジウム箔は、過酷な条件下でも柔軟で耐久性のある接着を維持するのに優れているため、RF およびマイクロ波システムなどの用途や高真空環境には欠かせません。微細な隙間を埋める能力により、高周波操作や極低温プロセスに不可欠な信頼性の高いシールが保証されます。インジウム箔の注目すべき利点には、不規則な表面に適合できる優れた延性と展性、および耐酸化性があります。
高性能ソリューションの重要性 コンピューターの冷却システムを最適化する場合、熱伝導率は重要な要素です。最高のパフォーマンスを求める人のために、Conductonaut は優れたソリューションを提供します。このサーマル コンパウンドは、非常に高い熱伝導率で知られており、効率的な熱放散が鍵となる厳しい構成に最適です。熱心なゲーマー、プロのデザイナー、または単にシステムに最高のものを求める人であっても、Conductonaut は熱管理を大幅に改善することを約束します。Conductonaut サーマル コンパウンドの利点 Conductonaut は、優れた熱伝導率により市場で際立っています。このサーマル ペーストは、最大 10 倍の熱伝導率を実現するように設計されています。
電子機器の熱管理では、最適なパフォーマンスと信頼性を確保するには、適切な熱伝導材料 (TIM) を使用することが重要です。近年人気が高まっている金属ベースの TIM の 1 つに、インジウム箔があります。この記事では、電子機器のアプリケーションで TIM としてインジウム箔を使用することの独自の特性と利点について説明します。熱伝導材料は、電子部品から熱を放散させて過熱を防ぐ重要な役割を果たします。高純度のインジウム金属から作られたインジウム箔は、86W/mK という優れた熱伝導率で知られています。この高い伝導率により、効率的な熱伝達が可能になり、電子機器の最適な動作温度を維持するのに役立ちます。インジウム金属…