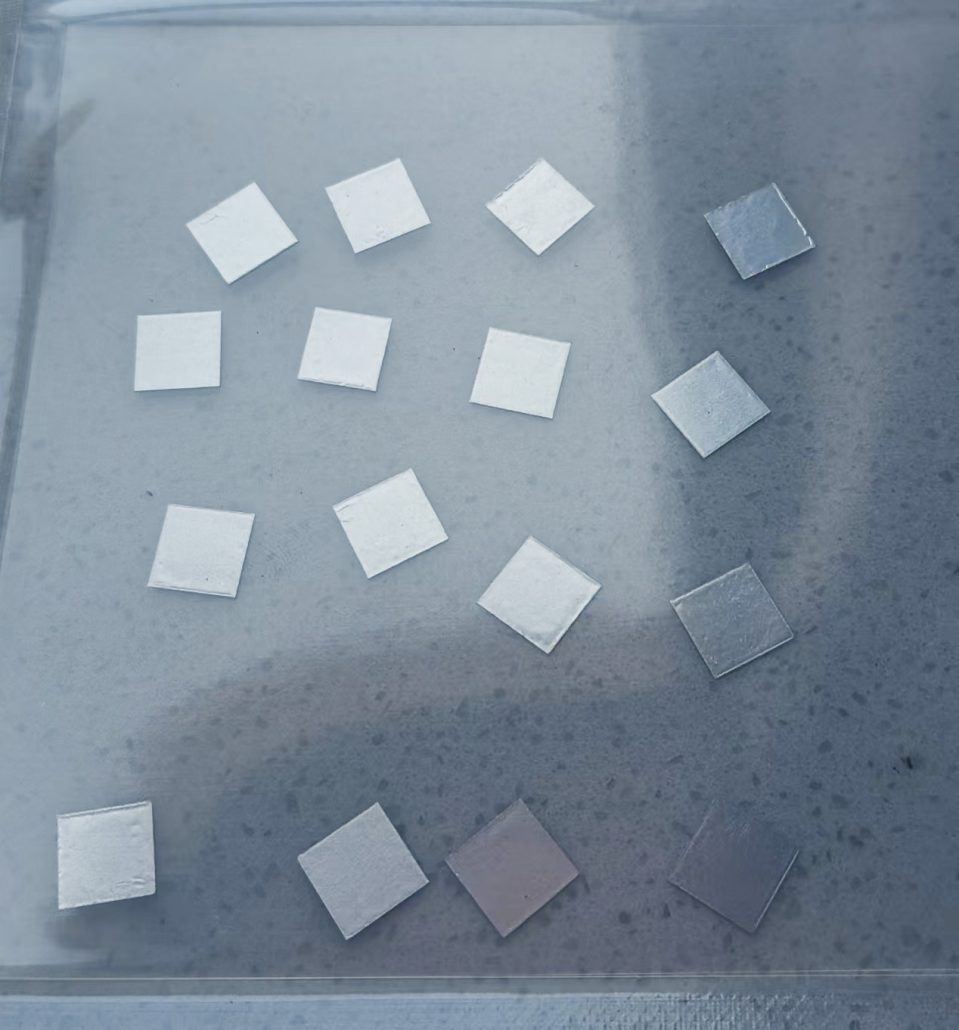
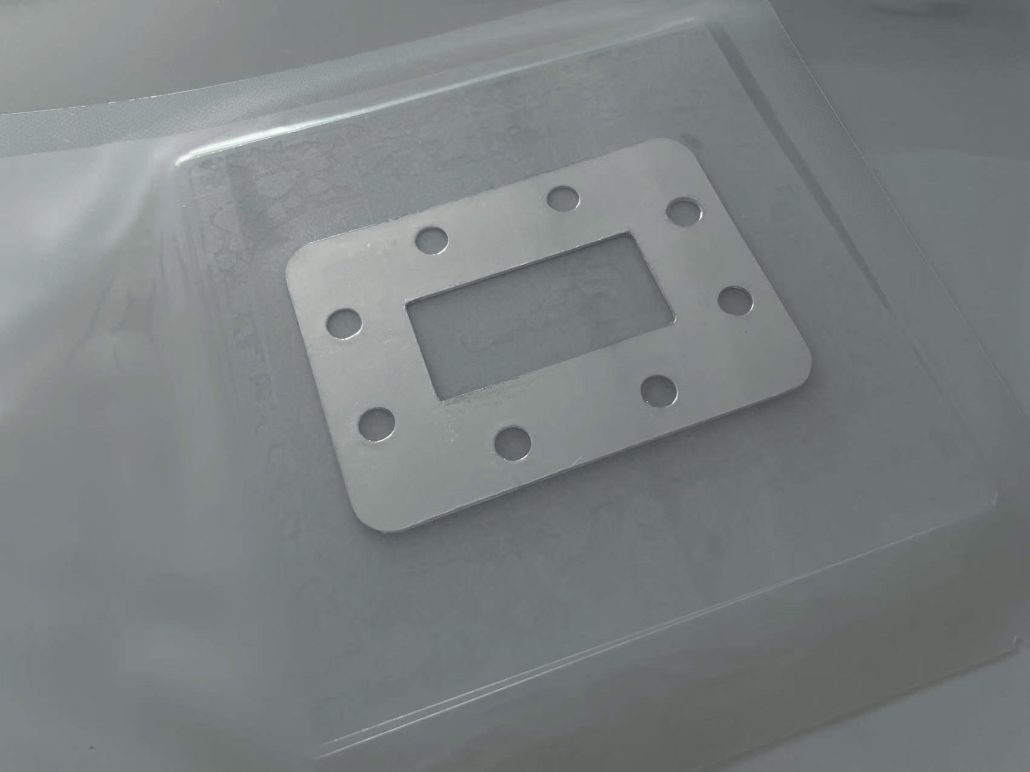
インジウム線はんだは、融点が低く、延性に優れ、熱疲労に強く、さまざまな材料と高い適合性があるため、精密電子機器やハイエンド製造においてかけがえのない役割を果たしています。以下は、その具体的な応用シナリオと利点の分析です。1. マイクロエレクトロニクスと半導体パッケージング温度に敏感な部品のはんだ付け用途: LED チップ、レーザーダイオード、MEMS (微小電気機械システム) センサー、その他の温度に敏感なデバイス。利点: インジウムは融点が低い (156.6°C) ため、高温による部品の損傷を防ぎ、はんだ付け後の熱応力を最小限に抑え、歩留まりを向上させます。高周波デバイスの相互接続用途: 5G 通信モジュール、マイクロ波および RF デバイス (GaN アンプなど)。利点: インジウムはんだは、安定した電気伝導性と低い信号損失を提供します…
はじめに 科学者はどのようにして物事を非常に低温に保つのか疑問に思ったことはありませんか? 絶対零度に近い温度では、最も頑丈な材料でさえ脆くなり、破損する可能性があります。 要求の厳しい極低温の世界では、超低温を達成して維持するには、特別なソリューションが必要です。 見落とされがちですが、非常に重要なコンポーネントの 1 つがシーリング材です。 ここで、インジウム箔/インジウムシール極低温技術が役立ちます。 柔らかく展性のある金属であるインジウムは、極寒で信頼性の高いシールを作成するのに非常に適した独自の特性を備えています。 この記事では、多くの極低温アプリケーションでインジウムが選ばれる理由について説明します。 極低温シールにインジウムを使用する理由 極低温シールの課題は、柔軟性を維持し、…
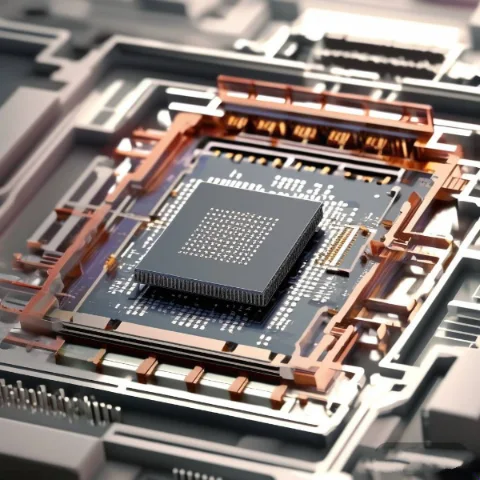
半導体パッケージングの世界では、熱管理はハイエンド プロセッサのパフォーマンスと信頼性を確保するための重要な要素です。プロセッサがより強力になり、より多くの熱を発生するようになるにつれて、高度な熱伝導材料 (TIM) の必要性が高まっています。主要なソリューションの 1 つがインジウム箔です。これは、優れた熱伝導性により半導体パッケージングに使用される高性能材料です。この記事では、インジウム シーリングの利点と用途、その仕組み、高性能チップのソリューションとして選ばれる理由について説明します。インジウム シーリングを使用する理由インジウム シーリングは、半導体パッケージ内のコンポーネント間の熱伝導材料としてインジウム箔またはインジウム シートを使用する方法です。従来の方法とは異なり…
急速に進化する今日のテクノロジーの世界では、CPU (中央処理装置) がコンピューターのパフォーマンスに重要な役割を果たしています。高速で効率的なプロセッサーの需要が高まるにつれて、CPU 製造におけるインジウム箔の使用が大きな注目を集めています。この記事では、CPU 用インジウム箔の世界を詳しく調べ、その利点、用途、この驚くべき素材を取り巻く複雑な詳細について説明します。CPU 用インジウム箔とは? インジウム箔は、優れた熱伝導性と電気伝導性で知られる希少金属であるインジウムの薄くて柔軟なシートです。CPU の性能を向上させる独自の特性により、エレクトロニクス業界、特に CPU 製造で広く使用されています。
電子部品を冷却しておくことは、パフォーマンスと寿命にとって非常に重要です。熱が蓄積すると、スロットル、不安定性、さらには永久的な損傷につながる可能性があります。そこで、熱伝導材料 (TIM) が役立ちます。これらの材料は、熱源 (CPU など) とヒートシンクの間の微細な隙間を埋め、効率的な熱伝達を促進します。利用可能なさまざまな TIM オプションの中で、インジウム箔と熱伝導ペーストはしばしば議論を巻き起こします。しかし、特定のアプリケーションにはどちらが適しているのでしょうか? 詳しく調べて、それぞれの特性、利点、および欠点を調べてみましょう。熱伝導材料 (TIM) について熱伝導材料は、2 つの固体表面間の空気の隙間を埋めるために不可欠です。空気は熱伝導率が低いため、これらの材料は…
はじめに 激しいゲーム、要求の厳しいソフトウェア、オーバークロック実験など、CPU を限界まで押し上げていますか? 熱はパフォーマンスの敵であり、従来の熱インターフェイス材料では不十分な場合があります。そこで、熱管理のゲームチェンジャーであるインジウム箔の登場です。この薄くて柔軟な金属シートは、優れた熱伝導性を提供し、CPU 温度を大幅に下げ、パフォーマンスを向上させます。この記事では、CPU 用のインジウム箔の世界を探り、その利点、用途、および考慮事項について詳しく説明します。インジウム箔とは何か、なぜ効果的なのか? インジウムは、優れた熱伝導性で知られる、希少で柔らかい銀白色の金属です。箔の形にすると、2 つの表面間で熱を伝達するための理想的なインターフェイス材料になります。以下は…
インジウム インターフェース材料とは? インジウム インターフェース材料は、熱管理アプリケーションで使用される特殊なソリューションで、熱伝達を高め、電子システムや産業システムで最適なパフォーマンスを確保します。これらの材料は、特に気密封止や極低温適合性を必要とする環境で、2 つの表面の間に信頼性が高く、効率的で耐久性のあるシールを作成する上で重要な役割を果たします。熱インターフェースの理解 熱インターフェースは、熱エネルギーが流れる 2 つのオブジェクト間の接続点です。例としては、ヒートシンクと熱電モジュール (TEC) の接合部があります。これらのインターフェースで最大の熱伝導率を達成することは、効率的な熱放散に不可欠であり、インジウムは多くのアプリケーションに理想的なソリューションを提供します。背後にある科学…
半導体パッケージングでは、高性能プロセッサで一般的に FCBGA (フリップチップ ボール グリッド アレイ) パッケージが使用されます。これらのプロセッサの消費電力が大きいため、より効率的な熱管理システムが必要です。優れた熱伝導率で知られるインジウム (In) は、大型パッケージ製品における従来の熱伝導材料 (TIM) の理想的な代替品として浮上しており、放熱性の向上が期待されています。FCBGA 市場の成長は、ネットワーク、自動車、AI、サーバーの需要によって牽引されています。2023 年、FCBGA パッケージング市場は約 $126 億 5,300 万に達しました。ネットワーク、自動車、人工知能 (AI)、サーバー インフラストラクチャなどの分野からの継続的な需要により、この市場は 2027 年までに $169 億に成長すると予測されており、年平均成長率 (CAGR) は…
効果的なチップ冷却の必要性 チップの消費電力と集積密度が増加するにつれて、発熱の増加に対処するための高度な冷却ソリューションの需要も増加しています。効率的なチップ冷却は、CPU や GPU から高密度半導体コンポーネントまで、電子デバイスの最適なパフォーマンスを確保し、寿命を延ばすために不可欠です。迅速かつ効果的な放熱がなければ、過熱によりデバイスのパフォーマンスが低下し、修復不可能な損傷につながる可能性があります。この記事では、高度なチップ冷却技術と、特にインジウムをベースとした金属ベースの熱伝導性材料 (TIM) の役割、および熱管理における低温合金材料の使用の増加について詳しく説明します。 1. チップ冷却技術の理解…
インジウムはんだの利点 インジウムはんだは、特にエレクトロニクス分野で、さまざまな産業用途で数多くの利点を提供します。その主な利点の 1 つは、高性能コンピューティング チップの熱管理における役割です。その高い熱伝導性と低い融点により、理想的な熱伝導性インターフェイス材料 (TIM) となります。これにより、効率的な熱放散が保証され、最適なデバイス パフォーマンスと寿命を維持するために不可欠です。電子アセンブリでは、インジウムはんだはその汎用性が特に高く評価されています。優れたシーリング機能により、赤外線デバイスのシーリングに広く使用され、デバイスの安定性と長期的な信頼性を保証します。さらに、高出力デバイスで TIM として使用すると、熱放散が向上し、寿命が長くなります。