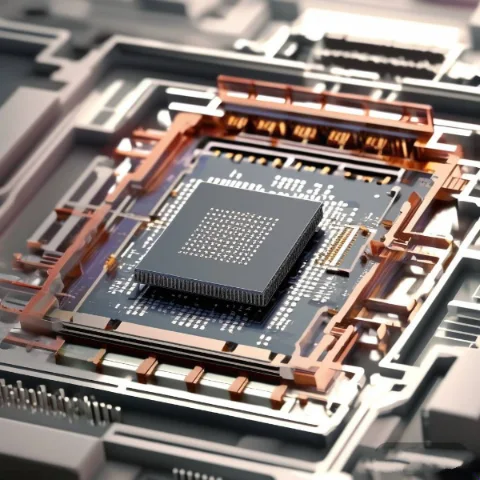
Indium wire solder plays an irreplaceable role in precision electronics and high-end manufacturing due to its low melting point, excellent ductility, resistance to thermal fatigue, and high compatibility with various materials. Below is an analysis of its specific application scenarios and advantages: 1. Microelectronics and Semiconductor Packaging Soldering of Temperature-Sensitive Components Applications: LED chips, laser…
Category Archives: Blog
Introduction Ever wondered how scientists keep things really cold? We’re talking temperatures approaching absolute zero, where even the most robust materials can become brittle and fail. In the demanding world of cryogenics, achieving and maintaining ultra-low temperatures requires specialized solutions. One of the often-overlooked but critically important components is the sealing material. That’s where Indium foil/Indium seal cryogenic technology…
In the world of semiconductor packaging, heat management is a critical factor for ensuring the performance and reliability of high-end processors. As processors become more powerful and generate more heat, the need for advanced thermal interface materials (TIM) has grown. One of the leading solutions is indium foil—a high-performance material used in semiconductor packaging for…
In today’s rapidly evolving technology landscape, CPUs (Central Processing Units) play a crucial role in the performance of our computers. With the increasing demand for high-speed and efficient processors, the use of indium foil in CPU manufacturing has gained significant attention. This article delves into the world of indium foil for CPU, exploring its benefits,…
Keeping your electronic components cool is crucial for performance and longevity. Heat buildup can lead to throttling, instability, and even permanent damage. That’s where thermal interface materials (TIMs) come in. These materials fill the microscopic gaps between heat sources (like a CPU) and heat sinks, facilitating efficient heat transfer. Among the various TIM options available, indium…
Introduction Are you pushing your CPU to its limits, whether through intense gaming, demanding software, or overclocking experiments? Heat is the enemy of performance, and traditional thermal interface materials sometimes fall short. Enter indium foil, a game-changer in thermal management. This thin, pliable metal sheet offers exceptional heat conductivity, promising significantly lower CPU temperatures and improved…
What Are Indium Interface Materials? Indium interface materials are specialized solutions used in thermal management applications to enhance heat transfer and ensure optimal performance in electronic and industrial systems. These materials play a crucial role in creating reliable, efficient, and durable seals between two surfaces, particularly in environments requiring hermetic sealing or cryogenic compatibility. Understanding…
In semiconductor packaging, high-performance processors commonly use FCBGA (Flip-Chip Ball Grid Array) packaging. Given the substantial power consumption of these processors, they require more efficient thermal management systems. Indium (In), known for its excellent thermal conductivity, has emerged as a potential ideal replacement for traditional thermal interface materials (TIM) in large-package products, promising enhanced heat…
The Need for Effective Chip Cooling As the power consumption and integration density of chips continue to increase, so does the demand for advanced cooling solutions to handle the rising heat generation. Efficient chip cooling is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and extending the lifespan of electronic devices, from CPUs and GPUs to high-density semiconductor…
Benefits of Indium Solder Indium solder provides numerous benefits across various industrial applications, especially in the electronics sector. One of its primary advantages is its role in thermal management for high-performance computing chips, where its high thermal conductivity and low melting point make it an ideal Thermal Interface Material (TIM). This ensures efficient heat dissipation,…