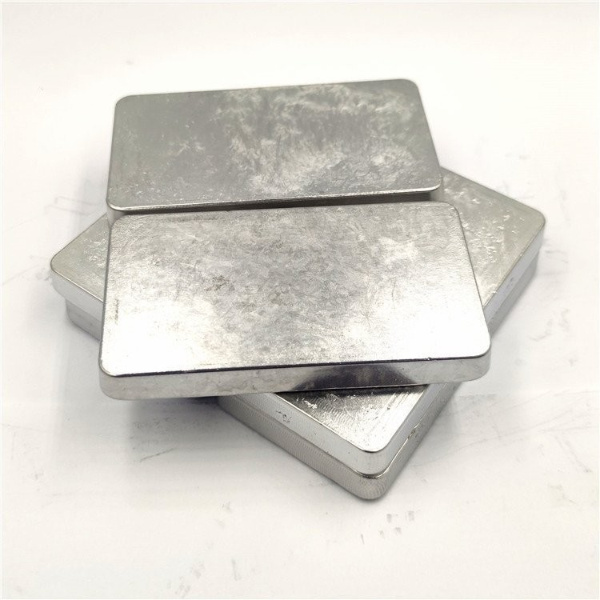
Indium-bismuth-tin alloy (In51Bi32.5Sn16.5) is a low-temperature eutectic alloy with a melting point of 60°C. This alloy is known for its excellent ductility and good thermal fatigue resistance. It is lead-free, cadmium-free, and environmentally friendly. The unique melting point of 60°C gives this alloy special applications; it can be used as a low-temperature liquid metal for heat dissipation in equipment. Additionally, it can be processed into powder and used as a filler in polymers to alter thermal resistance or as a special fuse material. We offer custom processing services for indium-bismuth-tin alloy, including indium-bismuth-tin granules, sheets, and wires.
| Alloy Ratio | In51Bi32.5Sn16.5 |
| Densité | 7.88g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 60°C |
| Thermal expansion coefficient | 22 |
| Thermal Conductivity | 25W/m/K |
| Tensile Strength | 33.44Mpa |
Customization
| Alloy Description | Liquidus* | Solidus* | Density* |
| Degrees oC/oF | Degrees oC/oF | gm/cm3 | |
| 49 Bi, 21 In, 18 Pb, 12 Sn | 58/136 | 58/136 | 9.01 |
| 51 In, 32.5 Bi, 16.5 Sn | 60/140 | 60/140 | 7.88 |
| 49 Bi, 18 Pb, 18 In, 15 Sn | 69/156 | 58/136 | 9 |
| 66.3 In, 33.7 Bi | 72/162 | 72/162 | 7.99 |
| 57 Bi, 26 In, 17 Sn | 79/174 | 79/174 | 8.54 |
| 54.0 Bi, 29.7 In, 16.3 Sn | 81/178 | 81/178 | 8.47 |
| 51.4 Bi, 31.4 Pb, 15.2 Sn, 2 In | 93/199 | 87/189 | 9.64 |
| 52 Bi, 31.7 Pb, 15.3 Sn, 1 In | 94/201 | 90/194 | 9.7 |
| 67 Bi, 33 In | 109/228 | 109/228 | 8.81 |
| 52 In, 48 Sn | 118/244 | 118/244 | 7.3 |
| 50 In, 50 Sn | 125/257 | 118/244 | 7.3 |
| 97 In, 3 Ag | 143/290 | 143/290 | 7.38 |
| 95 In, 5 Bi | 150/302 | 125/257 | 7.4 |
Low-melting-point alloys are mainly composed of elements like indium (In), tin (Sn), bismuth (Bi), lead (Pb), and cadmium (Cd). Alloys containing low-melting-point metals such as thallium (Tl), gallium (Ga), sodium (Na), indium (In), and mercury (Hg) are also considered low-melting-point alloys. In practical applications, alloys with a melting point below that of tin-lead eutectic (61.9% Sn-38.1% Pb, melting point 183°C) are generally classified as low-melting-point alloys. These alloys, containing elements like bismuth, lead, tin, cadmium, and indium, are widely used as solders, fuses, and thermal components in electrical, steam, fire protection, and fire alarm systems. As a new type of low-melting-point alloy material, they have significant development potential.
Applications:
- Medical Use: Primarily used to make radiation shielding blocks of specific shapes.
- Casting and Molding: Easily used for casting molds to produce special products or molds for specialized applications.
- Electronics and Electrical Automatic Control: Used as thermal-sensitive components, fuse materials, and fire alarm devices.
- Bending Metal Tubes: Used as a filler during the bending process of metal tubes.
- Metallographic Sample Preparation: Used as an embedding agent in metallographic sample preparation.