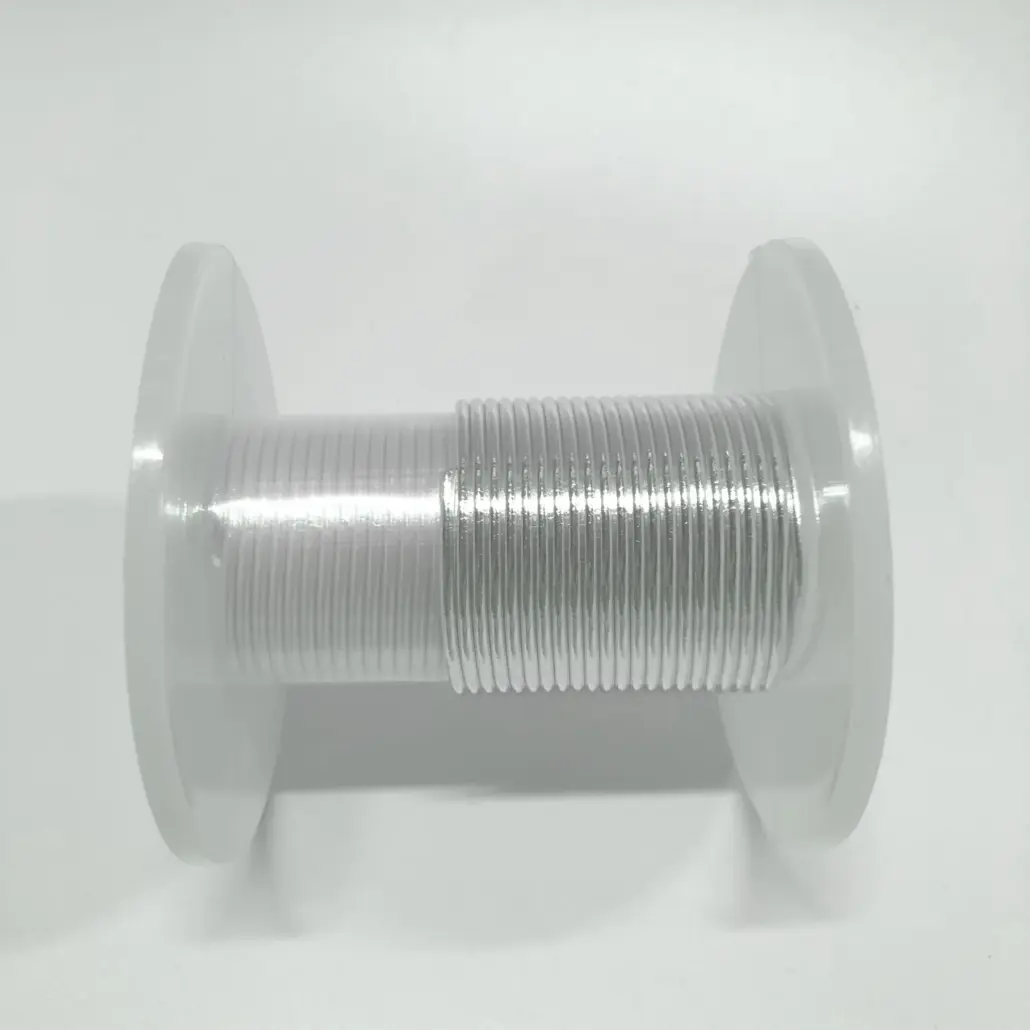
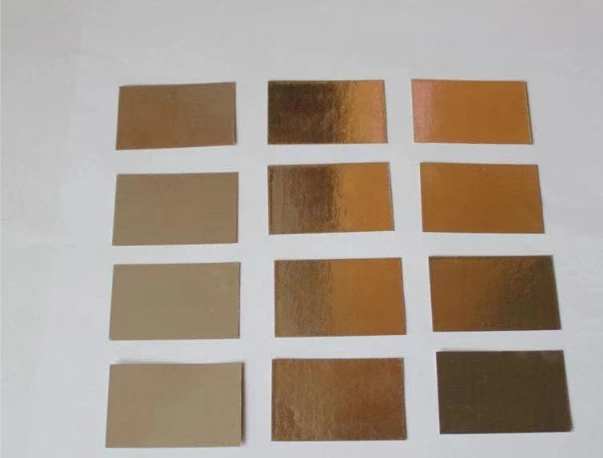
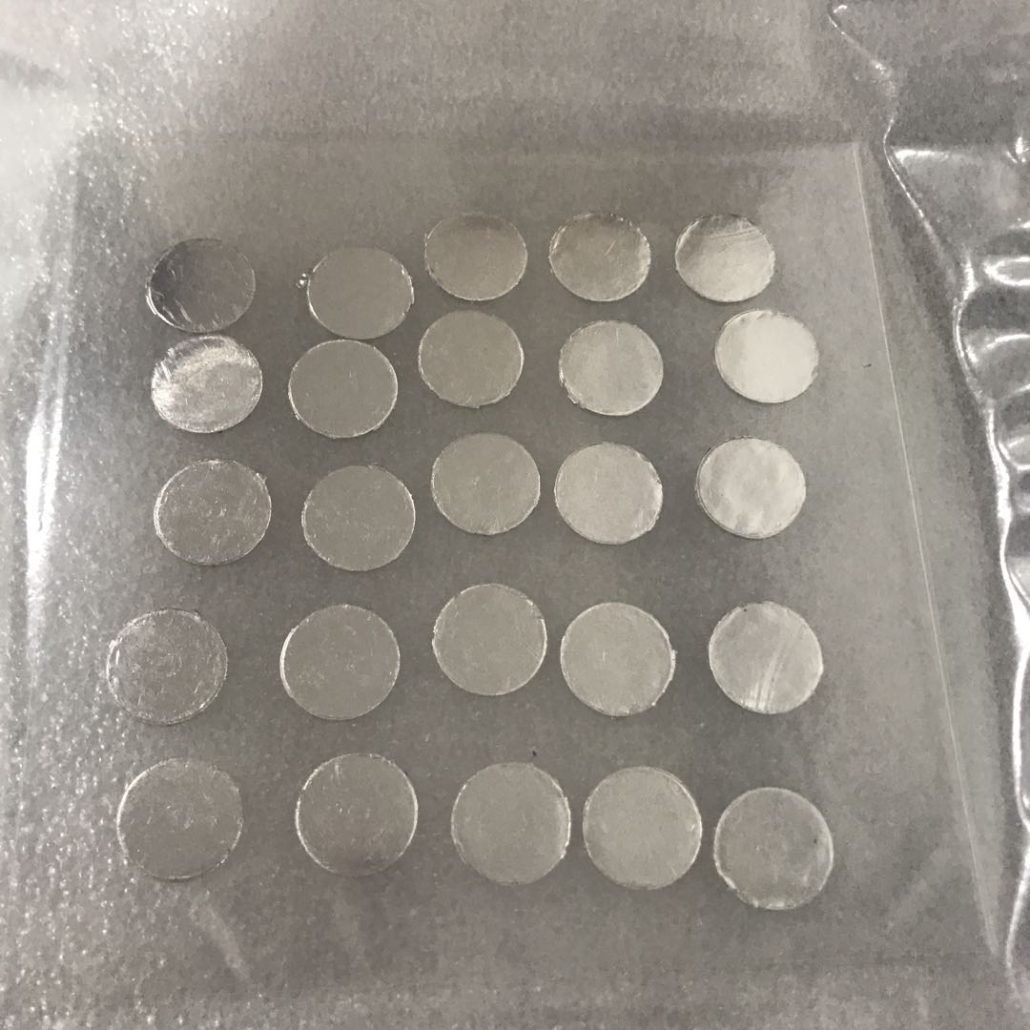
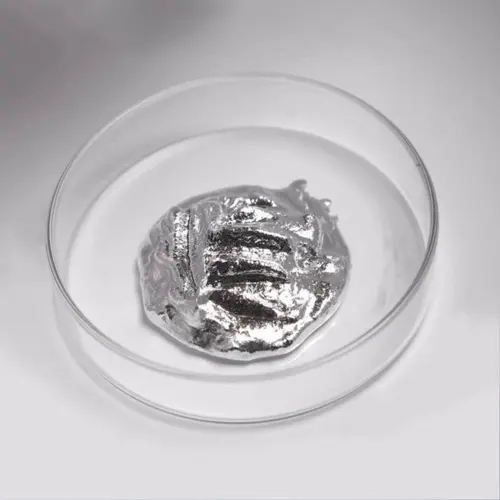
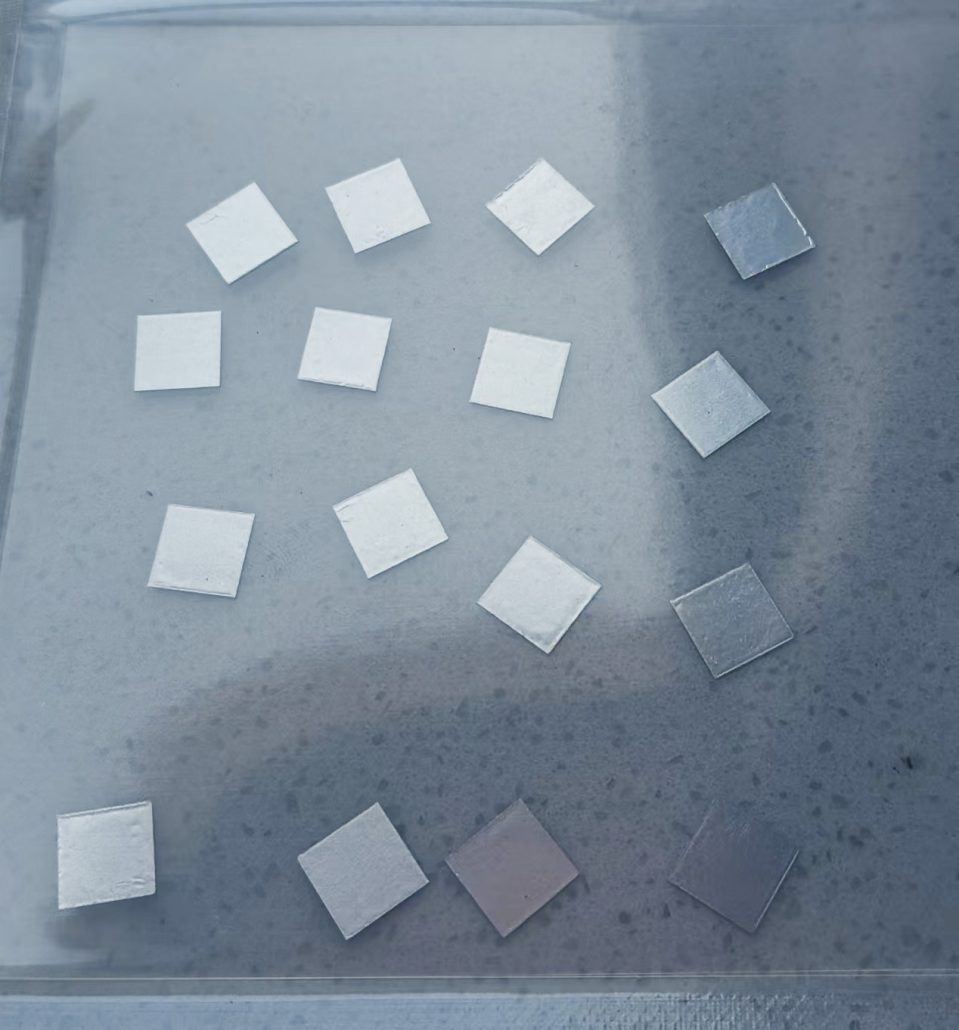
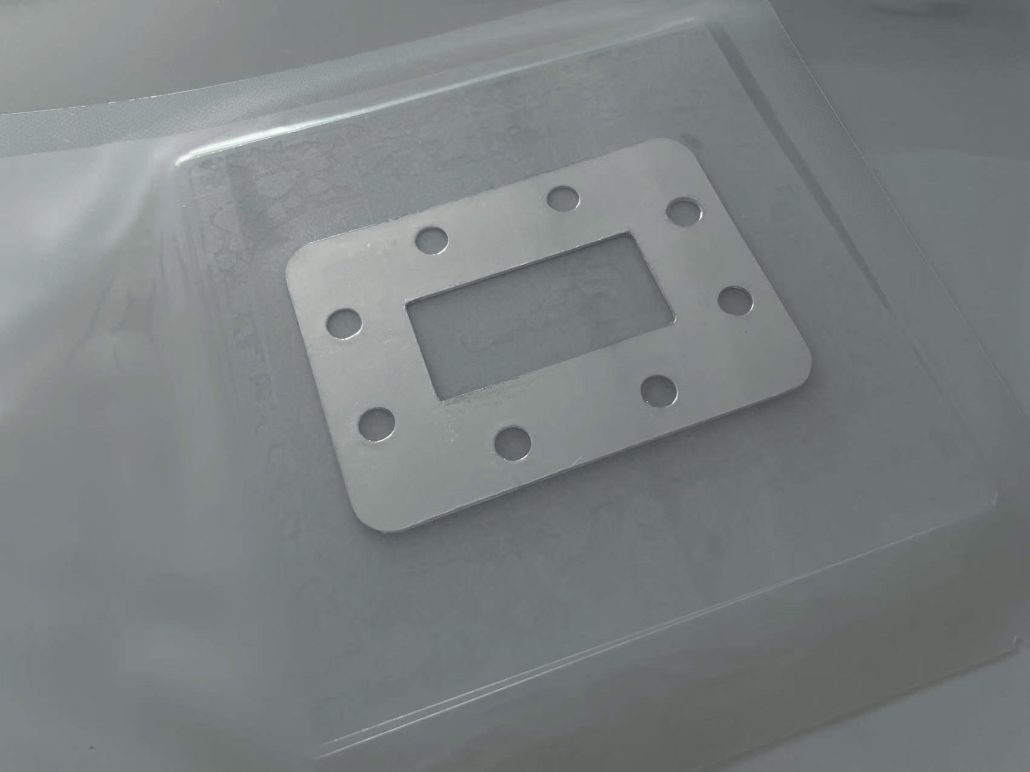
Indiumtrådslod spelar en oersättlig roll i precisionselektronik och avancerad tillverkning på grund av dess låga smältpunkt, utmärkta duktilitet, motståndskraft mot termisk utmattning och höga kompatibilitet med olika material. Nedan är en analys av dess specifika tillämpningsscenarier och fördelar: 1. Mikroelektronik och halvledarförpackningar Lödning av temperaturkänsliga komponenter Tillämpningar: LED-chips, laser...
Inledning Har du någonsin undrat hur forskare håller saker riktigt kallt? Vi pratar temperaturer som närmar sig absolut noll, där även de mest robusta materialen kan bli spröda och misslyckas. I den krävande kryogeniska världen kräver att uppnå och bibehålla ultralåga temperaturer specialiserade lösningar. En av de ofta förbisedda men kritiskt viktiga komponenterna är tätningsmaterialet. Det är där Indium folie/Indium tätning kryogen teknologi...
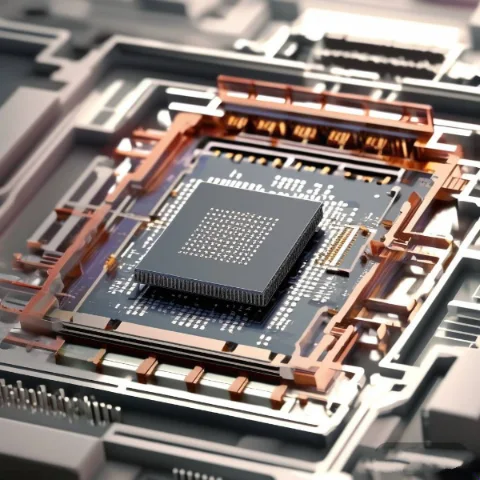
I en värld av halvledarförpackningar är värmehantering en kritisk faktor för att säkerställa prestanda och tillförlitlighet hos avancerade processorer. I takt med att processorer blir kraftfullare och genererar mer värme har behovet av avancerade termiska gränssnittsmaterial (TIM) ökat. En av de ledande lösningarna är indiumfolie – ett högpresterande material som används i halvledarförpackningar för...
I dagens snabbt utvecklande tekniklandskap spelar CPU:er (Central Processing Units) en avgörande roll för våra datorers prestanda. Med den ökande efterfrågan på höghastighets- och effektiva processorer har användningen av indiumfolie i CPU-tillverkning fått stor uppmärksamhet. Den här artikeln fördjupar sig i världen av indiumfolie för CPU och utforskar dess fördelar,...
Att hålla dina elektroniska komponenter svala är avgörande för prestanda och livslängd. Värmeuppbyggnad kan leda till strypning, instabilitet och till och med permanent skada. Det är där termiska gränssnittsmaterial (TIM) kommer in. Dessa material fyller de mikroskopiska luckorna mellan värmekällor (som en CPU) och kylflänsar, vilket underlättar effektiv värmeöverföring. Bland de olika tillgängliga TIM-alternativen, indium...
Introduktion Pressar du din CPU till dess gränser, vare sig genom intensivt spelande, krävande mjukvara eller överklockningsexperiment? Värme är prestandas fiende, och traditionella termiska gränssnittsmaterial misslyckas ibland. Gå in i indiumfolie, en spelomvandlare inom värmehantering. Denna tunna, böjliga metallplåt erbjuder exceptionell värmeledningsförmåga, lovar betydligt lägre CPU-temperaturer och förbättrad...
Vad är indiumgränssnittsmaterial? Indium-gränssnittsmaterial är specialiserade lösningar som används i värmehanteringstillämpningar för att förbättra värmeöverföringen och säkerställa optimal prestanda i elektroniska och industriella system. Dessa material spelar en avgörande roll för att skapa pålitliga, effektiva och hållbara tätningar mellan två ytor, särskilt i miljöer som kräver hermetisk tätning eller kryogen kompatibilitet. Förståelse…
I halvledarförpackningar använder högpresterande processorer vanligtvis FCBGA-förpackningar (Flip-Chip Ball Grid Array). Med tanke på den betydande strömförbrukningen hos dessa processorer kräver de effektivare värmeledningssystem. Indium (In), känt för sin utmärkta värmeledningsförmåga, har dykt upp som en potentiell idealisk ersättning för traditionella termiska gränssnittsmaterial (TIM) i stora paketprodukter, vilket lovar förbättrad värme...
Behovet av effektiv spånkylning I takt med att strömförbrukningen och integrationstätheten hos spånen fortsätter att öka, ökar också efterfrågan på avancerade kyllösningar för att hantera den ökande värmegenereringen. Effektiv chipkylning är avgörande för att säkerställa optimal prestanda och förlänga livslängden för elektroniska enheter, från CPU:er och GPU:er till högdensitetshalvledare...
Fördelar med indiumlödning Indiumlod ger många fördelar inom olika industriella tillämpningar, särskilt inom elektroniksektorn. En av dess främsta fördelar är dess roll i termisk hantering för högpresterande datorchips, där dess höga värmeledningsförmåga och låga smältpunkt gör det till ett idealiskt termiskt gränssnittsmaterial (TIM). Detta säkerställer effektiv värmeavledning,...